Most HI-FI artillery enthusiasts are interested in welding machines and motorcycles. But it is not enough to have a fever enthusiasm. You must have a certain electronic circuit foundation. Only in this way can you achieve a rational fever, not a real smoke machine. Based on my own nearly 20 years of fever experience, I have summarized the title of the basic knowledge of the minimum amplifier circuit required for HI-FI fever, and the detailed content needs to be studied and understood in detail.
1. Common amplifier components:
Bipolar transistor (NPN, PNP), field effect tube (junction field effect, insulated gate field effect, VMOS tube), composite tube (Darlington tube, IGBT tube), operational amplifier (voltage type, current type), It integrates successful release, thick film circuit, and fool circuit.
2. Common materials for manufacturing semiconductors:
Silicon (SI), germanium (GE), gallium (GA), the forward voltage drop of PN junction made of silicon material is 0.6-0.7V, the reverse withstand voltage can be more than 1000V, and the PN junction made of germanium material is positive The voltage drop is 0.2-0.3V, and the reverse withstand voltage is generally within 100V. Only germanium cannot be universally applied because the problem of the manufacturing process of germanium cannot be overcome. The biggest problem is that the thermal stability is not good, so there is no way to apply it in large quantities.
3. Three working states of the transistor:
The transistor has three states in the circuit: cut-off, amplification, and saturation. In the amplifier circuit, of course, we want the transistor to work in the amplified state. If the saturation or cut-off state is entered, saturation distortion or cut-off distortion (usually limiting distortion) In addition, because the forward conduction of the PN junction is nonlinear, switching distortion and crossover distortion will occur during the process from cut-off to amplification. The pure Class A power amplifier that everyone admires now is to make the transistor work in an amplified state, thereby reducing various distortions.
4. Three configurations of amplifier circuit:
Common emitter configuration, the most widely used, the signal is input from the base and the emitter, and output from the collector and the emitter. It has higher input resistance, larger voltage and current magnification, and wider frequency response, but the output resistance is relatively large.
In common base configuration, the signal is input from the emitter and base, and output from the collector and base. It has a wide frequency response and a higher voltage and current amplification factor, but the input resistance is small and the output resistance is large.
Common collector configuration, the signal is input from the base and the collector, and is output from the emitter and the collector, has a high input resistance, a low output resistance, a wide frequency response, but a voltage amplification factor Small (less than and close to 1) is a disadvantage of this configuration.
5. Single-ended amplification and push-pull amplification.
The output stage of a single-ended amplifier is composed of one amplifying element (or multiple elements but connected in parallel) to amplify the positive and negative signals for two and a half cycles. Single-ended amplifiers can only take Class A working conditions.
The output stage of the push-pull amplifier has two "arms" (two sets of amplification elements). When the current of one "arm" increases, the current of the other "arm" decreases, and the state of the two switches in turn. To the load, it seems that an "arm" is pushing and an "arm" is pulling together to complete the current output task. Although class A amplifiers can use push-pull amplification, it is more common to use push-pull amplification to form a class B or class A amplifier.
6. Differential amplifier circuit.
Use two identical tubes to form a two-half completely symmetrical circuit, generally working in a common emitter configuration. The signal is input from the base of the two tubes and the collector is output. This is the most basic differential amplifier circuit; The use of a differential amplifier circuit is mainly to suppress the "zero drift" that the circuit may produce and improve the temperature characteristics of the amplifier circuit.
Four basic connection methods for differential amplifier circuits: double-ended input and double-ended output, double-ended input and single-ended output, single-ended input and double-ended output, and single-ended input and single-ended output.
7. Typical applications of operational amplifiers:
We are mainly applying the linear amplifier circuit of the op amp. According to the connection form of the input signal, it can be divided into 3 cases:
The input of the reverse terminal, the circuit at this time has a certain depth of voltage parallel negative feedback. The characteristics of the circuit are: the input resistance is relatively small, the output resistance is very small, and the phase of the output signal and the input signal are opposite, and the common mode rejection ratio of the op amp is not high.
The input of the non-inverting terminal, at this time, the circuit has a certain depth of voltage series negative feedback. The characteristics of the circuit are: the input resistance is relatively large, the output resistance is very small, the phase of the output signal and the input signal are the same, and the common mode rejection ratio of the op amp is higher.
Differential input (the input signal of the non-inverting input terminal and the inverting input terminal are simultaneously input) is generally not widely used.
Clay artillery has a fever, and playing with the circuit itself is a pleasure. Why not do it by improving your knowledge by analyzing and improving the circuit?

Follow WeChat

Download Audiophile APP

Follow the audiophile class
related suggestion
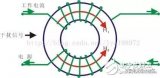
Common Mode Choke (Common Mode Choke), also called common mode inductor, is symmetrically wound on a closed magnetic ring in opposite directions ...
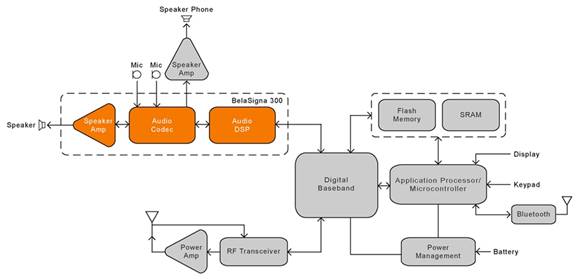
Advanced audio processing solutions provide Hi-Fi audio quality for portable communication devices using mobile phones, wireless headphones and integrated webcam microphones ...
Circuit basics 1, analog signals and digital signals: The object processed by electronic technology is an electrical signal that carries information, according to the characteristics of the signal ...
CD cable
To make the best effect of a sound system, it is not just to simplify them ...