Principle, classification, characteristic characteristics, parameters and application of humidity sensor
Human survival and social activities are closely related to humidity. With the development of modernization, it is difficult to find a field that has nothing to do with humidity. Due to different application fields, the technical requirements for humidity sensors are also different. From the manufacturing point of view, the same humidity sensor, material, structure, process is different. The performance and technical indicators (like accuracy) are very different, so the price is also very different. For the user, when choosing a humidity sensor, first of all, it is necessary to find out what kind of sensor is needed; what kind of product should be purchased under the circumstances that your financial resources allow, and weigh the relationship between “need and possibleâ€, not blindly. Acting. From the perspective of our interaction with users, I feel that the following issues are worth noting.

The water molecule affinity humidity sensor is a humidity sensor made of a water molecule having a large dipole moment and thus being easily adsorbed on a solid surface and penetrating into a solid interior (becoming a water molecule affinity), and the measuring principle is moisture sensing. The moisture absorbing or dehumidifying process of the material changes its own properties to form different types of humidity sensors.
Non-water molecular affinity humidity sensor, the main measurement principle is: the difference between the heat conduction of humid air and dry air is used to measure the humidity; the microwave is used to propagate in the air of water vapor, and the water vapor absorbs the microwave to cause a certain energy loss. The energy of the transmission loss is related to the humidity in the ambient air to measure the humidity; the water vapor can absorb the infrared rays of a specific wavelength to determine the humidity in the air.
Humidity includes the humidity of the gas and the humidity of the solid. The humidity of a gas refers to the content of water vapor in the atmosphere. The measurement method has absolute humidity, that is, the weight of water vapor contained per cubic meter of gas under standard conditions (0 ° C, 1 atm), that is, water vapor density; relative humidity, That is, the ratio of the partial pressure of water actually contained in a certain volume of gas to the maximum partial pressure of water vapor contained in the gas at the same temperature; or the moisture content, that is, the mass of water vapor per kg of dry air. Relative humidity is the most commonly used. The humidity of a solid is the percentage of the moisture contained in the substance, that is, the ratio of the mass of the water contained in the substance to its total mass.
A humidity sensor made of a water molecule having a large dipole moment and thus being easily adsorbed on a solid surface and penetrating into a solid interior is called a water molecule affinity humidity sensor, and the measuring principle is the moisture absorption or desorption process of the moisture sensitive material. Change its own performance to form different types of humidity sensors; humidity sensors that are independent of water molecule affinity are called non-aqueous molecular affinity sensors. The main measurement principle is: using the difference between the heat conduction of humid air and dry air Humidity; the use of microwaves to propagate in the air of water vapor, the water vapor absorbs microwaves to produce a certain energy loss, the energy of transmission loss is related to the humidity in the ambient air to determine the humidity; the water vapor can absorb the infrared rays of a specific wavelength To determine the humidity in the air.
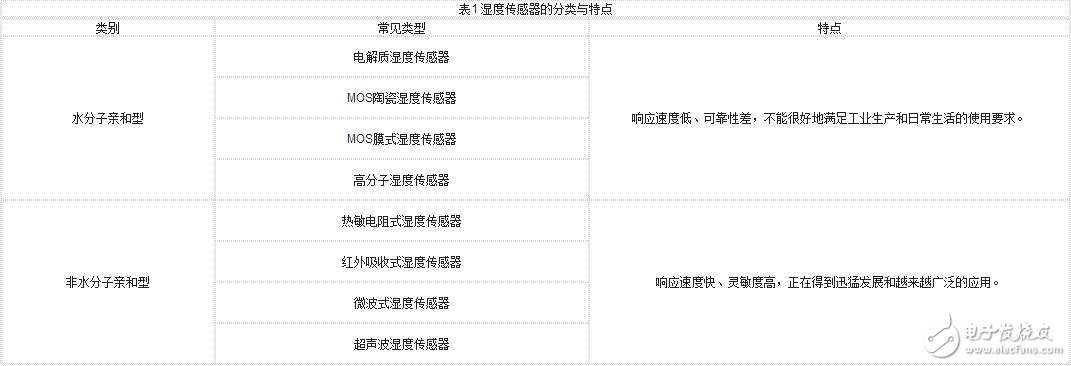
Classification and characteristics of humidity sensorsAccording to whether the sensitive scheme is based on the polar adsorption characteristics of water molecules, the humidity sensor can be classified into a water molecule affinity type and a non-water molecule affinity type. The water molecule affinity humidity sensor can be further classified according to the difference of the moisture sensitive material; according to the measurement principle, the nonaqueous molecule affinity humidity sensor can be further classified, as shown in Table 1.
1. Water molecule affinity humidity sensor
Water molecule affinity humidity sensors are classified into the following four types depending on the materials used.
(1) Electrolyte type: Taking lithium chloride as an example, it forms a pair of electrodes on an insulating substrate and is coated with a lithium chloride salt film. Lithium chloride is extremely deliquescent and produces ion conduction, which decreases with increasing humidity.
(2) Ceramic type: Generally, a porous ceramic is made by using a metal oxide as a raw material through a ceramic process. It is made by utilizing the resistance of the porous ceramic to the sensitivity of water vapor in the air.
(3) Polymer type: First, the comb electrode is evaporated on an insulating substrate such as glass, and a layer of organic polymer moisture sensitive film is adhered to the substrate by dipping or coating. There are many types of organic polymers, and the working principle is different.
(4) Single crystal semiconductor type: The material used is mainly a silicon single crystal, which is fabricated by a semiconductor process. Diode humidity sensitive devices and MOSFET humidity sensitive devices are made. It is characterized by its ease of integration with semiconductor circuits.
A typical water molecule affinity humidity sensor - lithium chloride resistance humidity sensor introduction:
Lithium chloride is an ionic inorganic salt which does not decompose, does not volatilize, and is stable in the atmosphere. The amount of moisture absorption is a function of the relative humidity of the air. As the relative humidity of the air changes, the amount of lithium chloride absorbs. When the lithium chloride solution absorbs water vapor, the number of conductive ions is increased, thus causing a decrease in electrical resistance; conversely, the electrical resistance is increased. This method of measuring the relative humidity of the air into its resistance value is called hygroscopic humidity measurement. The sensor of the lithium chloride resistance hygrometer works according to this principle. Its structure and resistance-wet characteristics are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively.

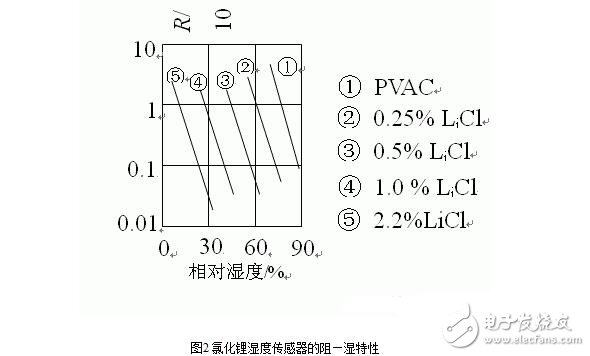
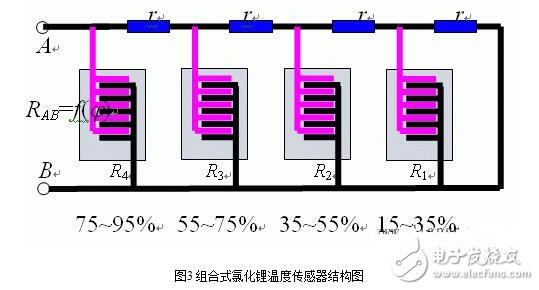
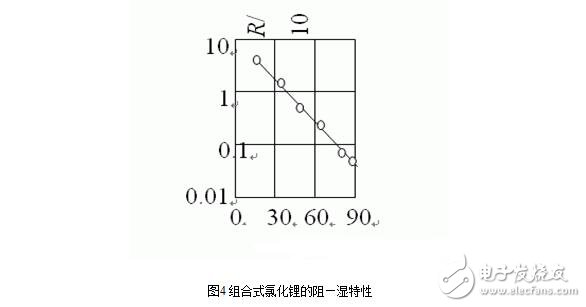
The humidity measurement range of the lithium chloride sensor is related to the concentration of lithium chloride applied and other components. An element fabricated at a certain concentration has an exponential relationship with the change in relative humidity of the surrounding air within its effective moisture sensing range. When the humidity is lower than its effective moisture absorption range, its resistance value increases rapidly and tends to be infinite; when it is higher than the range, its resistance value becomes very small, and even tends to zero. The measurement range of each sensor is narrow, so the corresponding range should be selected according to the requirements of the measurement range. To expand the measurement range, multiple combined sensors can be used. The structure and resistance-humidity characteristics of the combined lithium chloride humidity sensor are shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4.
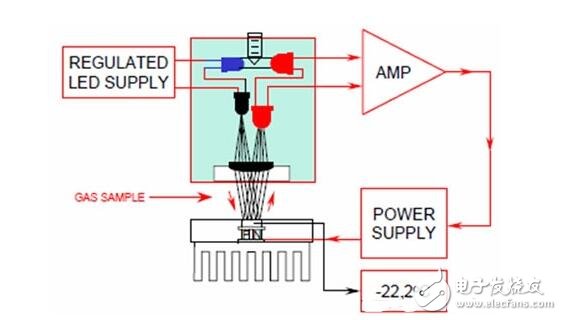
2. Non-aqueous molecular affinity humidity sensor
The difference between the heat conduction of humid air and dry air can be used to determine the humidity, which can be made into a thermistor-type humidity sensor; the correlation between the energy of transmission loss and the humidity in the ambient air when using microwave or ultrasonic wave to propagate in the air of water vapor To measure the humidity, it can be made into a microwave or ultrasonic humidity sensor; the water vapor can absorb the infrared light of a specific wavelength to measure the humidity in the air, and can be made into an infrared absorption type humidity sensor. The structure and working principle of a typical infrared absorption type humidity sensor are shown in Fig. 1.
Humidity sensor characteristic parametersThe characteristic parameters of the humidity sensor mainly include: humidity range, sensitivity, temperature coefficient, response time, wet hysteresis, wet characteristic quantity-relative humidity characteristic curve. ?
(1) Humidity range: It refers to the maximum range of ambient humidity that the humidity sensor can measure accurately. Due to the different materials used in various humidity sensors and the working principle of the various humidity sensors, their characteristics are not always applicable to the entire relative humidity range of 0 to 100% RH.
(2) Humidity characteristic quantity-relative humidity characteristic curve: The output variable of the humidity sensor is called the humidity characteristic quantity, such as resistance, capacitance, etc. The curve of the humidity characteristic of the humidity sensor as a function of the ambient humidity is called the sensor's moisture characteristic quantity-ambient humidity characteristic curve, which is simply referred to as the humidity characteristic curve. The moisture sensitive characteristic of a well-performing humidity sensitive device should have a wide linear range and moderate sensitivity.
(3) Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the humidity sensor is the slope of its moisture sensitivity curve. The humidity characteristic curve of most humidity sensitive devices is non-linear, so there is no uniform representation. A more common approach is to use the ratio of the wetted feature quantities of the device at different ambient humidity levels.
(4) Humidity temperature coefficient: It is defined as the rate of change of the relative humidity of the environment as a function of ambient temperature, which is expressed by the amount of moisture sensitive characteristic of the device.

Therefore, the ambient temperature will cause a humidity measurement error. For example, when α = 0.3% RH / °C, the temperature change of the environment is 20 ° C, which will cause a humidity error of 6% RH.
(5) Response time: It indicates the characteristic parameter of the time required for the sensor to complete the moisture absorption or desorption and the dynamic balance process when the ambient humidity changes. The response time is defined by the time constant τ, which is the time required for the wetted feature quantity to change from the starting value to 0.632 times the ending value. It can be seen that the response time is closely related to the starting and ending values ​​of the relative humidity of the environment.
(6) Wet hysteresis loop and wet hysteresis: The humidity characteristic curve of a humidity sensor in the case of moisture absorption and desorption is not repeated, and can generally be formed as a loop. This characteristic is called hysteresis characteristic. The curve is called the wet hysteresis loop.
Humidity sensor applicationThe work of any industry is inseparable from the air, and the humidity of the air is directly related to work, life and production, so that the monitoring and control of humidity becomes more and more important. The application of humidity sensor mainly has the following aspects:
(1) Climate monitoring Weather measurement and forecasting are of great significance to industrial and agricultural production, military and people's life and scientific experiments. Therefore, humidity sensors are essential moisture measuring devices, such as resin-expanded humidity sensors. Weather balloon measuring instrument on the wet.
(2) Greenhouse farming Modern agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and various industries have a considerable number of greenhouses. The humidity control of greenhouses is as important as temperature control. Controlling humidity in crops, trees, livestock and other suitable growth areas is to reduce pests and diseases and increase yield. One of the conditions.
(3) Industrial production In the textile, electronics, precision machinery, ceramics and other sectors, air humidity directly affects the quality and output of products, and must be effectively monitored and regulated.
(4) Storage of items Various items have certain adaptability to the environment. Too high or too low humidity will cause the item to lose its original performance. For example, in high-humidity areas, electronic products are seriously damaged in warehouses, non-metallic parts can be mildewed, and metal parts can corrode and rust.
(5) The use of precision instruments protects many precision instruments and equipments with high requirements on the working environment. The ambient humidity must be controlled within a certain range to ensure their normal operation and improve work efficiency and reliability. For example, the operating temperature of the telephone program-controlled switch is preferably 55 % ± 10%. If the temperature is too high, it will affect the insulation performance. If it is too low, it will easily generate static electricity and affect normal operation.
The Dell Latitude 3420 (also known as the E3420) is a business laptop designed for professionals who need a reliable and durable machine for their work. Here are some of its key features:
Processor: The laptop is powered by a 10th generation Intel Core i3, i5, or i7 processor, depending on the configuration you choose.
Memory: It comes with up to 16GB of DDR4 RAM, which ensures smooth multitasking and fast performance.
Storage: The laptop has a 2.5-inch drive bay that can accommodate a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, depending on your needs.
Display: The laptop has a 14-inch display with a resolution of 1366 x 768 pixels. You can also opt for a Full HD (1920 x 1080) display.
We provide DELL Latitude 3420 E3420 replacement parts, such as LCD Back cover; front bezel frame; palmrest with keyboard; bottom base enclosure lower cover etc, all the parts with brand new and original.
Dell latitude 3420 LCD back cover,Dell latitude 3420 parts,dell latitude 3420 replacement parts
S-yuan Electronic Technology Limited , https://www.syuanelectronic.com