SSD capacity
The final capacity size provided to the end user is in bytes. Remember that the nominal data is in decimal units. It is easy for people with programmer backgrounds to treat it as binary. For the same set of data, binary is better than decimal 7% more capacity, for example:
Decimal 128GB: 128 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 = 128,000,000 bytes
Binary 128GB: 128 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 = 137,438,953,472 bytes
The binary industry is called bare capacity, and the decimal is called user capacity. Bare capacity is about 7% more than user capacity.
This refers to GB. When entering the TB level, this value is greater. Readers can calculate by themselves.
For the flash memory itself, it provides capacity in binary. So, what does the 7% capacity of the binary naked capacity do inside the SSD? The SSD can use the extra 7% space to manage and store internal data, such as using this extra space as FTL mapping table storage space, reserved swap space required for garbage collection, and replacement space for bad flash blocks. The 7% extra space here can also become the OP concept (Over Provision), the formula is:

2
Media information
This is critical. The current core storage medium of SSD disks is flash memory. The semiconductor media such as flash memory has some limitations of its own physical characteristics, such as life cycle (PE cycles), program (write programming), Erase (erase) Read time, the effect of temperature on read and write, the size of the flash memory page, the size of the flash memory block ... These are the information of the media, the quality of the media directly affects the performance and integrity of the data storage.
Flash memory is divided into SLC, MLC, TLC (even QLC), which refers to the number of bits stored in a storage unit:
SLC = Single-Level Cell, that is, a single storage unit stores one bit of data. SLC is fast and has a long life span (approximately 50,000-100,000 rewrite lifetimes), but the price is super expensive (approximately more than 3 times the price of MLC).
MLC = Multi-Level Cell, that is, a single storage unit stores multiple bits (but generally refers to two bits) of data. The speed of MLC is average, the life is average (about 3k-10k times of erasing life), and the price is average.
TLC = Trinary-Level Cell, that is, a single storage unit stores three-bit data, and some flash memory manufacturers call it 8LC, which is slow, has a short life (about 500-1500 erase and write life), and is cheap.
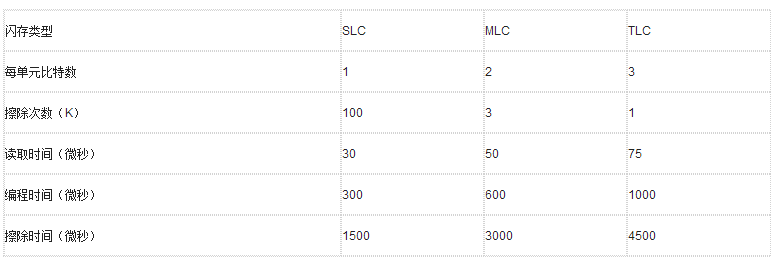
Table 1-1 Comparison of SLC, MLC and TLC parameters
The development of flash memory has experienced the great development of the 3D process from the 2D plane to the present. The goal is only one: the silicon unit area (mm2) can design and produce more bits (bits), so that the cost per GB The price is lower. This is the goal of media manufacturers and the demands of customers, and it is also the development trend of the semiconductor industry.
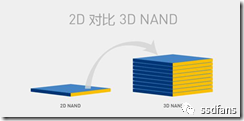
Figure 1-1 2D vs. 3D flash memory structure diagram
Looking at the comparison of the number of bits per unit area from 2D to 3D, 48-layer Samsung 3D V-NAND can produce 2600Mb of data per mm2, which is three times that of 2D flash memory, so the same wafer can cut 3 times the amount of data. With simple calculations, the price per GB can be reduced to 1/3.
Table 1-2 Comparison of different flash densities

Finally, let's take a look at the development node maps of flash memory. In a word, the ultimate goal of competition is to develop more dense, faster, and cheaper flash memory products within the scope of the process.

Figure 1-2 Flash memory factory roadmap
3
physical dimension
SSD is a standard part, and its external dimensions need to meet certain requirements (length, width, height, and interface connector), which is often called Form Factor. What form factors will the SSD have? It is subdivided into Form Factor standards such as 3.5-inch, 2.5-inch, 1.8-inch, M.2, PCIe card, mSATA, U.2, etc. Each Form Factor also has clear specifications such as measurements, weight, and interface pins.
Form Factor Standard Organization:
https: //
http: //

Figure 1-3 List of SSD dimensions
4
other
Here we look at the two parameters of temperature and certification and compatibility information.
All industrial products have temperature specifications, and SSDs should be used within a certain temperature range. Working temperature: 0 ℃ -70 ℃, it refers to the operating temperature of the SSD in the running state. Outside the temperature range of 0-70 degrees Celsius, the SSD may have product anomalies and data anomalies. Non-operating temperature: -50 ℃ -90C, the temperature during SSD storage and transportation, and the non-power-on working state, providing customers with temperature reference during product transportation and warehouse storage. If the temperature exceeds -50 ℃ -90 ℃, the SSD may be damaged.
Certification and compatibility information: SSD hardware and software should pass certain certification tests to reflect the standard testing of the product, and give customers clear information about whether they have passed the corresponding tests. Certification and compatibility are the test set of the corresponding standard organization. The standard organization belongs to a third party and is independent and objective. Passing the test means that part of the customer's test is eliminated.
Performance analysis
1
Performance
Hard disk performance indicators generally include IOPS (Input Output Operations Per Second, which reflects random read and write performance), throughput (Throughput, unit MB / s, which reflects sequential read and write performance), Response Time / Latency (response time / hour Extension, unit ms or us).
High Speed Blender,Ipl Laser Hair Removal,Diy Laser Hair Removal,Best Ipl Hair Removal,Epilator Ipl
SHENZHEN CHONDEKUAI TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD , http://www.siheyidz.com