U.S. thin TV specifications increasingly stringently accelerate LED TV market layout
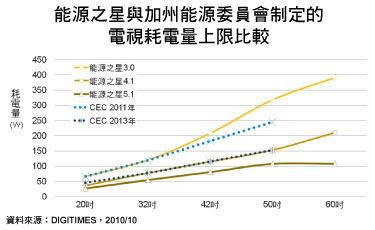 DIGITIMES Research pointed out that in the United States after the television has become thinner, the television power consumption of home TVs has risen due to factors such as the increase in the amount of television in consumers' homes and the size of TVs. This has caused the US government to consume power for thin TVs. Pay attention. Organizations such as the US Environmental Protection Agency and the California Government have set stricter standards for thin television power consumption and hope to increase the efficiency of home energy use by reducing the power consumption of thin TVs.
DIGITIMES Research pointed out that in the United States after the television has become thinner, the television power consumption of home TVs has risen due to factors such as the increase in the amount of television in consumers' homes and the size of TVs. This has caused the US government to consume power for thin TVs. Pay attention. Organizations such as the US Environmental Protection Agency and the California Government have set stricter standards for thin television power consumption and hope to increase the efficiency of home energy use by reducing the power consumption of thin TVs. The most representative energy-saving plan in the United States is the Energy Star. This plan began in 1992 and TV was incorporated into its specifications in 1996. The latest version of ENERGY STAR 4.1 was implemented in May 2010. Its TV power consumption limit has been significantly reduced by 35% to 50% compared to the previous version of ENERGY STAR 3.0, and ENERGY STAR 5.1 is expected to be implemented in 2013. The TV power consumption ceiling is even lower than Energy Star 4.1 by 30% to 35%, and the maximum power consumption of large-size TVs larger than 50 inches will be 108W.
The Californian government of the United States also expects to implement thin television energy efficiency laws and regulations starting in January 2011. Although its power consumption standards are looser than that of Energy Star, it is different from the Energy Star’s initiative of participating in the voluntary scheme of the company. California’s thin television energy efficiency laws and regulations Coercive forces that stipulate that products that do not meet energy efficiency standards will be prohibited from selling in California.
In addition to the thin TV energy efficiency specifications, the US Environmental Protection Agency is also expected to announce in July 2011 the environmental performance indicator IEEE 1680.3 related to the use of toxic substances in thin television products, product life, and waste management. Due to the toxicity of mercury, the implementation of this standard may limit the use of mercury-containing CCFL backlights, which will accelerate the development of LED TVs.
Shenzhen Ever-smart Sensor Technology Co., LTD , https://www.fluhandy.com