1 Introduction
Chongqing is one of the six old industrial bases in China, and is also the birthplace of modern industry in Southwest China and an important industrial city in China [1, 2]. During the 11th Five-Year Plan period, Chongqing has built 41 municipal-level industrial parks. From January to September 2011, these parks achieved a total industrial output value of 57.06 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 45.7%. In 2011, the planned fixed industrial investment was 150 billion yuan. In the first half of the year, industrial fixed investment was 75.57 billion yuan, of which the park completed infrastructure investment of 13.86 billion yuan. As of September, the city's industrial park has newly built 1,644,000 square meters of standard factory buildings (excluding the construction and rental of factory buildings), and has built a total of 838,900 square meters of standard factory buildings [3]. In the new round of the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†of Chongqing, “the five major trillions of industrial sectors will be formed by 2020â€, and the corresponding industrial construction will receive more policy support and development space in the next few years. With the development of industrial parks, energy consumption has also increased: In 2009, the comprehensive energy consumption of industrial enterprises above designated size was 2767. 01 × 10 000 tons of standard coal, accounting for 43% of the total energy consumption of the city; The comprehensive energy consumption is 3207. 27 × 10 000 tons of standard coal, accounting for 45% of the total energy consumption of the city [4]. In the context of the ever-increasing energy crisis, how industrial plant design can reduce energy consumption while effectively improving the indoor physical environment is a problem worthy of further discussion.
Making full use of natural light can not only reduce lighting energy consumption, but also help users' physical and mental health and improve work and study efficiency. Due to the non-visual effect of the human eye, spectral differences can affect the circadian rhythm, body temperature, and alertness of the human body, which in turn affects work efficiency and human health [5]. Tom DeMarco et al. found that the office environment under natural lighting can significantly improve people's work efficiency and work ability [6]. A sample of 141 medical nurses conducted by MustafaKemal Alimoglu et al. found that at least 3 hours of daylight exposure per day helped reduce work stress and job satisfaction [7]. Therefore, how to introduce more high-quality and reasonable natural light on the premise of energy-saving and humanized design, while taking into account the light and thermal environment, is a key point in the design and transformation of modern factories.
The main sources of natural light in single-storey buildings are side lighting and top lighting. Due to the large span and depth of single-storey buildings, top lighting (sunlight lighting) can more effectively improve the utilization of natural light. There are three main types of common sunroof: rectangular sunroof, zigzag sunroof and flat skylight. Domestic scholars have conducted comparative studies on these three types of skylights, such as: Wang Gang and Shao Wei of Shandong Jianzhu University, etc. compared the parameters such as the ratio of window to window and the number of sunroofs and spacing to the lighting index, uniformity and light direction of the indoor stadium. The influence of sex, etc. [8]. Peng Peng and Zheng Jie of Chongqing University analyzed the changes of cooling, heating and lighting energy consumption of different skylight areas [9]; Yan Yonghong and Wang Ning further studied the best of the skylight through energy simulation software. Window range ratio and arrangement [10]; Peng Xiaoyun of East China Jiaotong University analyzed the relationship between sunroof type, dip angle, orientation and energy consumption [11]. Studies have shown that flat skylights have the highest light extraction efficiency, but glare and overheating problems are difficult to solve; rectangular skylights and zigzag skylights have slightly lower light extraction efficiency, but have obvious advantages in terms of uniformity of illumination, prevention of glare and control of heat intake. The author investigates the actual use of these kinds of skylights in single-storey buildings in Chongqing, and hopes to find out the types of skylights that are more suitable for the climate characteristics of Chongqing, and further optimize the design.
2 Investigation on the current situation of skylighting in single-storey factory buildings in Chongqing
The author selected some single-storey buildings in the Industrial Park of Chayuan New District of Chongqing for field investigation and related data collection and analysis.
The planned area of ​​Chongqing Chayuan Industrial Park is 120 square kilometers, mainly for mechanical equipment and electronic (IT) manufacturing (see Figure 1). The type of skylight in a single-storey factory building in the park is mostly flat skylights, with a small number of rectangular skylights and no zigzag skylights. Five typical single-storey workshops built after 2005 were selected to investigate the current status of natural daylighting.

2. 1 Research content
2. 1. 1 Research object
5 single-storey buildings in Chongqing Tea Garden Industrial Park
2. 1. 2 Research content
(1) Natural light harvesting conditions and skylight patterns in typical areas of the factory building;
(2) Indoor and outdoor temperature and humidity;
(3) Evaluation of the photothermal environment in the plant throughout the year.
2. 1. 3 Measurement tools and methods
(1) Indoor and outdoor temperature and humidity: measured by Nissan KANOMAX air quality detector;
(2) Indoor and external illumination values: measured by a domestic remote YF2006 illuminometer;
(3) Subjective evaluation of indoor lighting conditions and summer thermal comfort conditions: Questionnaire survey was used.
2. 2 Survey results and analysis
The five single-storey buildings surveyed are machined workshops, and the current status of lighting is shown in Figure 2. Among them, the three workshops A, B and C are cloudy and have light rain on the day; D and E are two different typical areas of the same joint factory, and the measurement day is cloudy.

2. 2. 1 Survey data and subjective evaluation
The status of daylighting and ventilation in the five workshops was tested. By issuing questionnaires, workers were given corresponding evaluations on the physical environment of the space (lightness, glare, ventilation, thermal environment), and typical of the five workshops. The area has been collected for light and heat data. This article only lists the survey data of the lighting section (see Table 1):
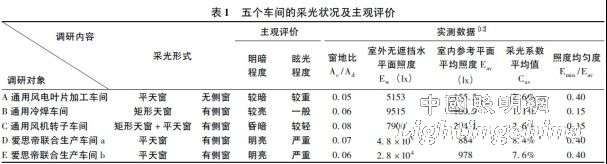
Note: 1. The measurement time is from 14: 00 to 16: 10 per day.
2. The influence of machinery and equipment on lighting is available in all measurement areas. Therefore, the lighting coefficient is corrected according to the actual situation [12].
3. Subjective evaluation: The surveyed objects are workers at all points in the factory (no less than 30 people in each area), and five levels of brightness and glare are evaluated.
2. 2. 2 Analysis of survey results
Among the five tested workshops, the B workshop used a rectangular skylight, and the workers in the survey reported that the workshop was the darkest. Comparing the two workshops of B and E, in the case of the same window, the lighting coefficient, illuminance uniformity and average illuminance value of the E workshop are better than the B workshop, but the glare is heavier than the B workshop. It proves that the efficiency of the flat skylight is significantly higher than that of the rectangular sunroof, but how to solve the glare problem is a more difficult problem. This is further evidenced by the analysis of three test data from the A, D, and E workshops using flat skylights.
In the five workshops, the workers reflected that the illuminance was acceptable and the glare was light, and it was the only workshop in which the combination sunroof was used.
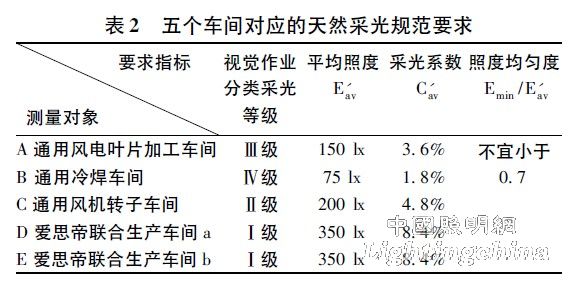
According to (GB / T 50033-2001) "Building Lighting Design Standards", the above five workshops should meet the requirements of Table 2:
Comparing Table 1, it can be seen that although the average indoor illuminance values ​​of the five workshops in the survey basically meet the requirements of the specification, the lighting coefficient and illuminance uniformity have not met the specification requirements (only the lighting coefficient of the D workshop is up to standard). The questionnaire survey shows that space users (workers) are generally dissatisfied with the light and thermal environment. They believe that there are insufficient light in many areas of the workshop, while other areas are severely glare, and all workshops have summer overheating problems.
2. 3 Research conclusions
Through this survey, combined with the visits to relevant design institutes in Chongqing, the problems of natural lighting in single-storey buildings in Chongqing are summarized as follows:
(1) The natural lighting conditions of existing single-storey buildings in Chongqing are not ideal. The more prominent problem is that the lighting coefficient and illuminance uniformity index do not meet the national standard requirements, and many indoor working areas must be supplemented by artificial lighting.
(2) The flat skylights of the three types of sunroof types are the most widely used, but the same standardized sunroof products used in other regions do not take into account regional climate differences, and indoor glare and summer overheating problems are difficult to solve. The combined performance of the combined sunroof is better than a single flat sunroof, but it is less used in practice.
(3) There is a general lack of support for building physical technology during the design stage of the plant. When designing roofing and lighting, the design relies mainly on experience and standard drawings, resulting in poor light and thermal environment.
3 Single-storey factory for skylight type analysis
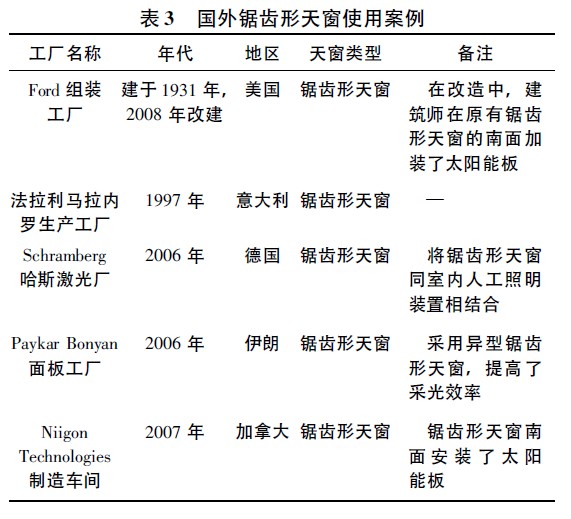
3. 1 Foreign factory skylight lighting case
In contrast to domestic production, the use of serrated sunroofs is common in foreign single-storey buildings (see Table 3). The following are some of the cases collected by the author (Figure 3 ~ Figure 7). It can be seen that there are many types of workshops with zigzag sunroofs, but these zigzag skylights have been improved on the basis of traditional sunroofs, which makes the lighting efficiency very good. Great improvement.
Compared with the domestic zigzag sunroof, the foreign zigzag sunroof is more mature and diversified in terms of the structure and installation method, and the combination with other devices (such as artificial lighting devices, roof solar panels). The above examples also prove that the traditional skylight form has been improved and upgraded to meet the high standard indoor light and thermal environment requirements of modern industrial plants.


3. 2 Analysis of the type of skylight used in single-storey buildings
The advantages of the flat skylight are high lighting efficiency, simple structure and convenient construction, which are suitable for various plant structure forms. However, its defects are also very obvious: the uniformity of illumination is poor, the glare is severe, the illumination changes drastically, and the skylight is rich in form, which can create a rich and interesting indoor space environment, which is conducive to shaping high quality, outstanding features and more humanity. Modern factory environment.

4 Zigzag sunroof optimization exploration
At present, the zigzag sunroof has not been widely used in various single-storey factory buildings in China. The main reason is that the lighting efficiency is lower than that of the flat skylight, and the other reason is that the structure and construction are relatively complicated and the cost is high. Since the traditional flat sunroof has been used for many years in the country, the development of the zigzag sunroof frame and the corresponding supporting components has not been developed, which has caused the design, development, manufacture and application of the zigzag sunroof to lag behind the current situation abroad. To change this situation, we must first solve the problem of how to effectively improve the lighting efficiency through reasonable optimization of design.


4. 1 Improve lighting efficiency and light environment quality
4. 1. 1 Material Optimization
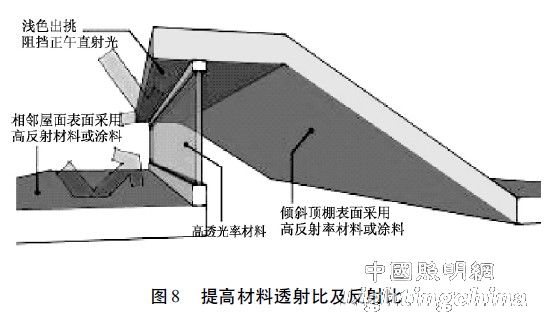
The zigzag skylight usually consists of a slanted reflective surface, two triangular sides and a windowed surface. In order to ensure the lighting efficiency, the light-emitting material with high transmittance and the indoor surface material with high reflectance should be selected. As shown in Fig. 8, the lighting efficiency can be improved by increasing the slope reflection surface and the adjacent roof reflection ratio.
4. 1. 2 Structural optimization
(1) Changing the curvature of the inclined surface to enhance the diffuse reflection of light can improve the lighting efficiency and improve the uniformity of lighting. Figure 9 shows the simulation results of the Ecotect software.
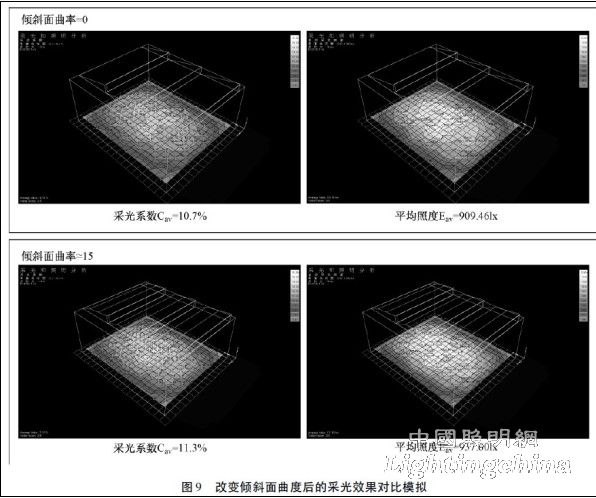
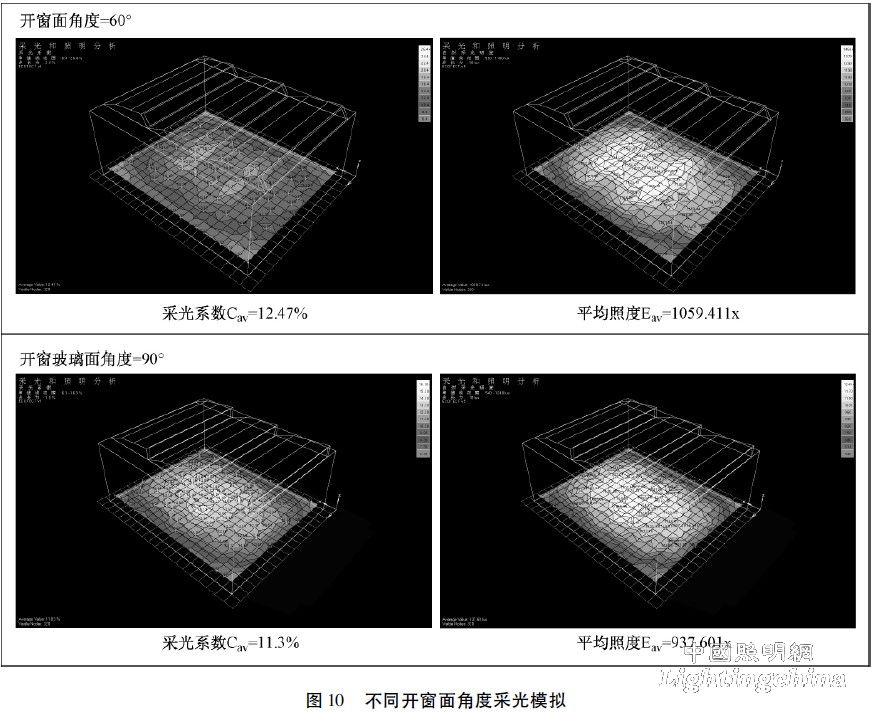
2) Changing the angle of the window opening can also effectively improve the lighting efficiency, as shown in Figure 10. Experiments have shown that when the daylighting efficiency is 2%, the window-opening area with a certain inclination of the glass surface is reduced by about 1/3 [13] compared with the glass surface. The comparative simulation results of the Ecotect software prove this, as shown in Figure 10. In this way, it is necessary to strengthen the rain protection measures.
4. 1. 3 Adding auxiliary lighting components
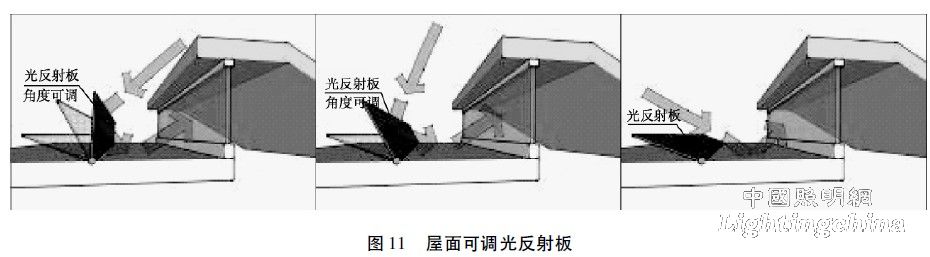
(1) Roof dimmable reflector
The zigzag sunroof is a one-way lighting system, and there may be weak lighting at certain times of the day, regardless of orientation. Place the roof light reflector in a suitable location for more reflected light. The reflector can be a high reflectivity material such as an aluminum sheet, and the reflector should be angled as needed to accommodate changes in the solar elevation angle at different times (see Figure 11).
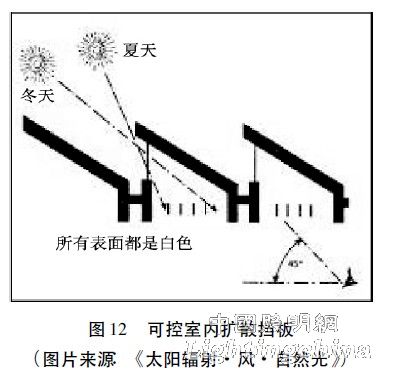
(2) Controllable indoor diffusion baffle
The use of an indoor diffusion baffle on the one hand makes the light distribution in the working area more uniform and on the other hand avoids direct glare. The baffle spacing is designed to prevent direct sunlight in the midday, while also considering the fact that when the sun's elevation angle is low, there is no direct sunlight into the human eye. As shown in Figure 12 [14]. The baffle material is typically a highly reflective translucent matte material.
4. 2 Skylights - Building Energy Efficiency Integration Measures
4. 2. 1 Lighting energy saving
(1) Combination of natural lighting and artificial lighting
The sensor is arranged near the zigzag sunroof, and the continuous dimming mode of the artificial intelligence control system is used to adjust the illumination level of the artificial illumination according to the change of the natural illumination degree, so that the indoor illumination level is always maintained in a moderate area. This measure can effectively reduce the lighting energy consumption.
(2) Combination with solar energy
Combining the zigzag sunroof with the solar device to realize the utilization of solar energy is also a commonly used means in the integrated design of building energy conservation in recent years. Zigzag sunroofs provide an ideal location for solar energy conversion: for example, solar photovoltaic panels can be placed on the inclined surface of the skylight to provide an energy source for artificial lighting; and with the emergence of solar glass that can both transmit light and generate electricity, The zigzag skylight has been upgraded from a simple daylighting function to a versatile energy harvester; if the solar cell battery that is currently under development is commercialized in the near future, the cost of solar energy utilization can be greatly reduced, which is beneficial to the new type. The promotion of multi-functional zigzag sunroof.
4. 2. 2 Improve thermal performance
Compared with the flat skylight, the zigzag skylight can provide a better indoor light environment. If it is properly designed, the indoor thermal environment can be greatly improved by improving the skylight structure and selecting the lighting material with superior thermal performance. improve. For example, in the internal structure design of the sunroof, the shielding of direct sunlight in summer is considered. The new energy-saving glass with good thermal performance, such as Low-E glass and dimming glass, reduces the heat intake in summer and the escape of heat in the winter.
5 Conclusion
At present, the indoor light and heat environment of single-storey buildings in Chongqing are generally poor, and the skylights are in a single form. The research in this paper shows that the flat skylights used in practice are not suitable for Chongqing, and the zigzag skylights have better light and thermal performance. However, the main reason why the zigzag sunroof is difficult to promote is that, firstly, the lack of professional lighting design team in the architectural design process, the design institute used the design pattern of the previous factory in the lighting design according to the convention, resulting in the factory lighting mode for decades. Second, because the architects lacked sufficient understanding of the new skylight form of the factory, the skylight manufacturers lacked motivation to develop new products. Therefore, even if a few architects or lighting experts want to use a new type of jagged sunroof with better performance, they can't buy a suitable finished product, and they can't find a construction unit with enough experience to carry out the construction. To change this situation, we need the joint efforts of architects, lighting experts and production companies.
It is a tough job to research, develop and promote new multi-functional zigzag sunroofs. This article has only carried out preliminary explorations, aiming to attract more attention from experts in related fields, and work together to improve the light and heat environment of the plant and provide workers with energy-saving, environmentally friendly and more humane working environment.
The project is supported by the school-enterprise cooperation project “Study on Natural Lighting and Indoor Lighting of Industrial Plants in Chongqing†(Shenzhen Jinliang Industrial Co., Ltd.), “Jialing Group Corporation's overall relocation and technical transformation project joint workshop/modeling room skylight lighting and indoor lighting Research (China Machinery Industry Third Design and Research Institute) project funding. Thank you to the partners here!
Edit; Nizi
What is Feeder on the placement machine? What is Feida on the placement machine? Feida is the main accessory of the placement machine. Its function is to mount the SMD patch components on the feeder, and the feeder provides components for the placement machine for patching.
In the placement machine, the feeder functions to supply the chip component SMC/SMD to the placement head in a regular pattern and order for accurate and convenient pickup, which occupies a large number and position in the placement machine. It is also an important part of choosing a placement machine and arranging the placement process. Depending on the SMC/SMD package, feeders typically have a variety of tapes, sticks, waffles, and bulk materials.
Tape feeders with the different size such as 8mm, 16mm, 24mm, 32mm, 44mm, 56mm etc.Panasonic Feeder,Insertion Machine Tape Feeder Unit,Tape Feeder Unit,Feeder Panasonic
Shenzhen Keith Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.aismtks.com