At present, the development of mobile phones has become the common focus of the global electronics industry. In addition to the voice and camera functions, the next step of the mobile phone is obviously to incorporate the entertainment functions of video multimedia. This is a fairly groundbreaking concept and technical challenge. The future of mobile phones will not only be a phone, camera or game console, but also a "television set" that will be taken with you.
This article refers to the address: http://
Mobile Radio and TV Specs Competition
In order for mobile phones to have the function of watching mobile broadcast television, there are currently three ways to go: multimedia multicast/broadcast services over 2.5 G/3G wireless networks; digital multimedia broadcast (DMB) work on the spectrum of digital audio broadcasts; A handheld device broadcast standard extending from the microwave digital television standard is employed.
  
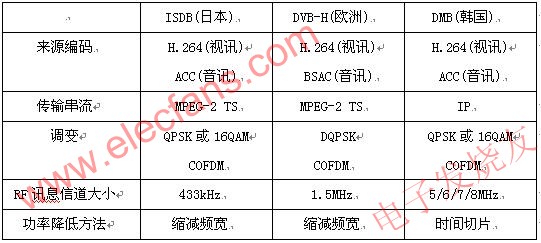
Table 1 list of mobile broadcast standards
In these three scenarios, due to the limited bandwidth of 2.5 G/3G and the high cost, it is not an excellent choice to use it to watch TV. However, in China, China Mobile and China Unicom have launched stream-based streaming. Media technology mobile TV business, in which China Mobile is on its GPRS network, China Unicom is relying on its CDMA1X network.
The DMB led by South Korea can be divided into T-DMB using terrestrial broadcasting and S-DMB using satellite. It has been improved by Eureka-147 DAB technology that has been used in Korea for nearly ten years. Among them, T-DMB uses ITU-T H.264 encoding technology for video, and uses MPEG-4 bit-slice arithmetic coding technology for audio. Then, it uses MPEG-4 synchronization layer and MPEG-2 transmission stream. They are multitasking along with additional data. South Korea’s mobile radio TV, which was scheduled to launch DMB technology at the end of 2004, is quite fast.
DVB-H is popular
However, since it is watching TV, playing through the existing TV system can be said to be a way of pushing the boat. There are three major specifications for digital TV standards that have been implemented globally for many years, namely DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) in Europe, Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) in the United States, and ISDB (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting) in Japan. The possibility of integration of mobile communication and digital broadcasting networks, so in September 2002, it was proposed to develop a video standard (DVB-Handheld, DVB-H) suitable for handheld devices, and in January 2004, the basics of the specification were developed. The framework then went into validation and standardization procedures in February. Due to the rapid development of DVB-H, related technologies such as US regulations and Japanese regulations are also moving closer to it.
  
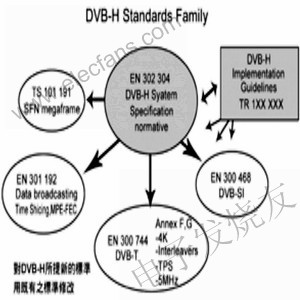
Â
Figure 1 Diagram of the DVB-H standard family
DVB-H is based on terrestrial digital video broadcasting (DVB-Terrestrial, DVB-T) transmission technology for home TV reception, so it retains some compatibility with DVB-T receiving circuits, but it is suitable for handheld devices to receive video. Features such as low power consumption, high mobility, uninterrupted common platform and network switching services, etc., to ensure normal viewing in indoor, outdoor, walking or driving cars, DVB-H has done a lot of technology Improve.
The goal of DVB-H in power consumption is to control the total power consumption of antennas, TV tuners and OFDM decoding circuits below 100mW. In contrast, indoor TVs are not sensitive to power consumption, DVB -T plans to reduce the indicator to 600mW in 2007.
Japanese single band specification
In the development of TV mobile phones, although it is dominated by European technology, in the development and application of products, Japanese manufacturers are at the forefront. Japan's planned mobile TV broadcasting practice is to develop a proprietary terrestrial digital TV standard based on its ISDB, which is the ISDB-T single-band broadcast transmission specification. There are many similarities between single-band transmission and DVB-H specifications, but there are still some differences. For example, DVB-H uses time-slicing to improve transmission quality, and single-band transmission is based on frequency division. deal with.
Single-band transmission uses the UHF band (470M_770MHz) to transmit radio waves, each of which is allocated a bandwidth of approximately 5.6MHz. The TV station then divides the allocated bandwidth into 13 bands, each of which is about 433 kHz, and can transmit up to about 21 Mbps of digital data. At this speed, each band can transmit 1920 x 1080 pixels of MPEG-2 format high quality programs. However, not all of these 13 frequency bands are allocated to ordinary indoor televisions, and one of the frequency bands in the middle is used for digital televisions for handheld devices, providing a transmission speed of approximately 200K_300Kbps.
Handheld device design challenges
For handheld devices to really watch digital video, its internal system design needs to pass some harsh tests, such as compression coding, TV signal receiving components (receiver, tuner, antenna, etc.) size, overall power consumption and reception. Features, etc.
Compression coding
Due to the limited bandwidth, video compression technology must be relied upon to achieve acceptable video quality in small windows. To this end, DVB-H has examined a variety of video compression formats, and the most popular one is H.264/MPE G-4 AVC (H.264) format.
Compared with other compression formats, H.264 has more advantages, it can achieve high compression, its compression rate is 2_3 times of MPEG-2, 1.5 times _2 times of MPEG-4; if it is used to transmit mobile The information can be transmitted at a rate of less than 200 Kbps for 15 frames per second of QVGA format. In theory, the handheld device can process the incoming video program with only a processor of about 125 MHz.
At present, the encoding method of video compression is not specified in the DVB-H specification, and the broadcast television operator can choose MPEG-4 or H.264. Uncertainty in specifications is a headache for developers who receive signal functions. They always want to develop products that can be used globally. In this case, the industry may adopt software to maintain the flexibility of the decoding function, but The processing power of the software is worse after all.
Small size challenge
To receive microwave digital TV signals on handheld devices such as mobile phones, the antenna (Antenna), Receiver data read demodulation LSI, UHF (UHF) tuner and other components are all indispensable. They used to be used in TV sets. They don't have to worry too much about shrinking the size. But today, they need to be plugged into a handheld device that is much smaller than a TV set, and they must have the same function. The difficulty is conceivable. know.
According to the trial samples that have been published, the size of the signal receiving part developed by NEC and Sanyo Electric is about 30mm long, 20mm wide and 2mm thick except for the size of the antenna. The world's smallest Sony component is 20mm long and 16mm wide. Although it is a little smaller, the size is still too large, and the industry believes that the ideal size is at least 10mm square the same as the FM audio tuner equipped with the mobile phone.
Reduce power consumption
Another key bottleneck is the power consumption of handheld devices when watching TV. Video multimedia has always been the most resource-intensive content, and it is an unacceptable burden for small-sized devices with handheld power. In terms of the current capacity of mobile phone lithium batteries, it is about 700 mA/h, and the power consumption of hand-held telecommunication signal receiving devices that are trial-produced by today's manufacturers is between 200mW and 150mW (such as NEC and Sony products). Watching TV programs under such specifications, the ideal maximum time is only 90 minutes, and there is no power for a long time.
However, at the time of viewing, in addition to the signal receiving component, the color screen of the mobile phone is also in full-load operation, so the power consumption is further increased. Ka Tengming, research director of the NEC System Platform Research Institute, pointed out that if there is no technical breakthrough, such as the use of fuel cells, the problem of insufficient battery power of mobile phones cannot be solved temporarily. In this case, the developer has to extend the TV viewing time, and can only start from reducing the excess function of the mobile phone in the viewing, or the power saving measures such as the tuner circuit being turned off in the time of receiving the video.
Improve antenna receiving function
To effectively improve the receiving sensitivity of handheld devices to microwave digital TVs, an effective method is to use "Diversity Reception". Its principle is to equip the handheld device with two different antennas to receive the TV signal at the same time, and then use the one with better signal quality.
At present, the most promising approach is to use the original telescopic whip antenna of the mobile phone and the "earphone antenna" of the earphone cable. As a result, there are two locations for receiving TV signals, even if one antenna is more The received signal is disordered due to reasons such as multipath interference, and the received signal of the other antenna can be used, so that the television signal can be stably received. Sanyo Electric's previously introduced TV mobile phone prototype uses a dual antenna to receive TV signals. However, this method consumes more power, and its TV tuner module requires 250mW of power.
in conclusion
Although the application of TV mobile phones has not yet fully developed, it seems that various hardware manufacturers are gearing up and ready to enter the market to eat this fat new market. There are still many technical challenges ahead of them. However, this is the best survival rule in this market: who can take the lead in removing technical barriers and win the market favor.
Breakout Cable,Multi-Purpose Break-Out Cable,Anti-Water Anti-Ultraviolet Radiation,Harmless To Environment
Shandong Qingguo Optical Fiber Co., Ltd. , https://www.qgfiber.com