Foreword: In the past, LEDs can only be used as the status indicator. The heat dissipation of the package has never been a problem. However, in recent years, the brightness and power of LEDs have been actively improved, and they have been used in applications such as backlighting and electronic lighting. The problem of package heat dissipation has quietly emerged.
The above-mentioned teachings are somewhat confusing. Isn’t the brightness of LEDs ever exceeded today? In 2003, Lumileds LighTIng's Roland Haitz based on an empirical technical inference law based on past observations, starting from the first commercial LED in 1965, in the development of these 30 years, LED is about every 18 months. In 24 months, the brightness can be doubled, and in the next 10 years, the brightness can be increased by 20 times, and the cost will be reduced to 1/10 of the existing one. This is also the Haitz law that has been popular in recent years. It is considered to be the Moore law of the LED industry.
According to Haitz's law, LEDs with a brightness of 100 lm/W (100 lumens per watt) appeared around 2008 and 2010, but the actual development seems to be more advanced than the law. June 2006 Nichia Chemical Industry (Nichia) Engineering samples up to 100lm/W white LEDs have been available and are expected to be officially put into mass production by the end of the year.
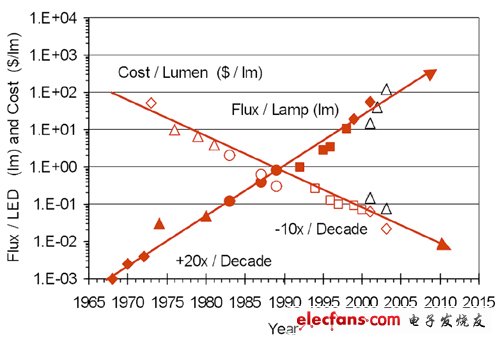
Remarks: Haitz's law can be said to be the Moore's law in the LED field. According to Roland Haitz, LEDs can double the luminous efficiency in almost 1824 months in the past 30 years, and thus estimate the next 10 years (2003) 2013) will grow 20 times more brightness, but the price will be only 1/10 of the current price.
Not only the brightness continues to increase, but also the heat dissipation technology of LED has been improved. In 1992, the thermal resistance of an LED was 360 °C / W, and then dropped to 125 ° C / W, 75 ° C / W, 15 ° C / W, Now it is at the point of 6 °C / W10 °C / W. More simply, in the past, for every watt of power consumed by LED, the temperature will increase by 360 °C. Now it consumes 1 watt of electricity, but the temperature only rises by 6. °C10 °C.
A small number of high-brightness, multiple and dense arrangements are the main cause of heat increase
Since the brightness efficiency is improved and the heat dissipation efficiency is improved, isn't it more contradictory? Should there be no more heat dissipation problems? In fact, it should be said more strictly that the heat dissipation problem is not high brightness, but high power; not in traditional packaging, but in new packaging and new applications.
First of all, in the past, it was only used as the LED of the indicator light. The current of each single (light conduction) is between 5mA and 30mA, which is typically 20mA. Now the high-power LED (Note 1) is Each single will have a current of 330mA1A, and each "power consumption" is increased by ten times or even tens of times (Note 2).
Note 1: In the practice of existing high-power LEDs, in addition to increasing the area of ​​single-emitting bare crystals, there are also practices in which multiple bare crystals are packaged together. In fact, some white LEDs are three kinds of bare crystals of red, green and blue in the same package to mix white light.
Note 2: Although the lighting (sudden conduction) voltages of various LEDs are different, this difference is temporarily ignored here.
When the multiplied current is sent in the same single package, the heat will naturally double, so the heat dissipation will certainly deteriorate, but unfortunately, because the white LED is used as the flash of the camera phone, it is used for small lighting. It is not enough to use a light bulb to make a lighting bulb inside the projector. It is not enough to use high brightness, and high power is used. At this time, heat dissipation becomes a problem.
The above LED application method uses only a few high-power LEDs, about 14 flashes, about 18 illumination bulbs, and more than 10 projectors, but the flash has less chance of use, and the lighting time is not long, single illumination. The light bulb has a relatively large space for heat dissipation, but the projector does not have ample heat dissipation space but can be equipped with a cooling fan.
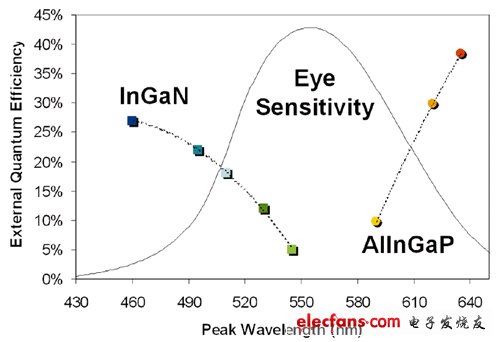
Remarks: In the figure, the semiconductor materials used for InGaN and AlInGaP LEDs, the external quantization efficiency map at each peak wavelength (light color), although ideally can approach 40%, but if the light extraction efficiency is included Considering that it is actually between 15% and 25%, not to mention that the two materials in the more efficient part are not in the category of human eye sensitivity, only 20% under the category.
However, there are still many applications that require high brightness, but need to use high-brightness LEDs intensively, such as traffic lights, message lights, video walls made up of LED groups, etc. It is not easy to dissipate heat, which is the heat dissipation problem caused by the application.
What's more, in the backlight of LCD TVs, it is not only the use of high-brightness LEDs, but also densely arranged, and in order to pay attention to the short and light, the heat dissipation design space available on the back is more limited, and should not be considered if the requirements of high standards are met. Use a cooling fan, because the noise of the fan will affect the taste of TV viewing.
Infrared Optical,Zinc Selenide Lens,Optical Zinc Selenide Lens,Optical Imaging Lens
Danyang Horse Optical Co., Ltd , https://www.dyhorseoptical.com