When studying the development trend of mobile TV technology, it is necessary to distinguish the product function combination, packaging, performance, semiconductor technology used and the most important RF receiver performance. At present, most single-mode demodulators are manufactured using 130 nm to 65 nm CMOS processes.
In most cases, they are packaged with a radio frequency receiver in a system-in-package (SiP) to form a mobile TV front-end component. However, the performance of different solutions is different, and sooner or later these products will only meet their respective transmission standards.
In "time slot mode" (including radio frequency and memory suitable for multi-service applications), the main challenges for achieving extremely low system power consumption of less than 50mW are the small form factor and the integration of the system on the consumer electronics platform. the complexity. However, as the market matures, the biggest challenge is to meet the needs of shortening the development cycle and reducing production costs. In order to meet the above challenges, Infineon Technologies developed the OmniVia TUS9090.
System Features
TUS9090 is an innovative monolithic IC developed using Infineon's RFCMOS 130-nanometer process. The SOC integrates multi-band radio frequency receivers (VHF, UHF and L-band for EU and North America), DVB-T demodulator components and DVB-H physical layer and embedded memory required for firmware and multi-service data reception .
TUS9090 does not require external filters, memory and other components, but if TUS9090 is used to receive DVB-T in the VHF band, an external LNA is required. TUS9090 integrates on-chip memory and logic core, with various link layer and FEC functions. Table 1 compares the DVB-H system with other newly developed systems.
To develop this mixed-signal monolithic IC requires a lot of engineering expertise and rich experience. First, you need to partition the system. You need to analyze the performance requirements during partitioning, and then implement the best hybrid partition of software and hardware according to the needs. Subsequent design optimization requires the implementation of advanced signal processing algorithms, but engineers need to understand the related noise issues—noise emitted by high-speed digital components can enter sensitive analog RF components (such as LNA). If the design is not careful and the tests are not detailed enough, the system robustness requirements cannot be met, resulting in reduced performance and ultimately disappointing the customer. In addition, due to adjacent channel interference, rapid deep attenuation of the signal (the terminal moves with cars and trains), and poor indoor received signal strength (signal power loss), mobile TV reception is facing severe challenges.
The innovative TUS9090 single-chip IC fully complies with the MBRAI II specification. In DVB-H mode (QPSK, CR 1/2, GI = 1/4, 8MHz, 8K FFT), the RF sensitivity is higher than -98dBm. If the external balun is not included, the noise figure of the RF tuner is 4dB. Under the condition of TU6 channel (MPE frame error rate is 5%), assuming the use of QPSK modulation, 1/2 code rate, 1/4 guard interval, 3/4 MPE FEC rate and 8K FFT, the minimum carrier-to-noise ratio (C / N) is 8.4dB. Under the same conditions, the phase shift Fd3dB @ MBRAI is 170Hz. Similar performance can be achieved under single frequency network (SFN) conditions.
TUS9090 adopts 8.5 & TImes; 8.5 & TImes; 0.8mm SGA package. However, in order to minimize the overall size, the TUS9090 monolithic chip is packaged in bumps and supplied in the form of bare chips (the thickness of the bump die is less than 0.4mm), which facilitates the development of very small modules at low cost. Eliminating the packaging process, further reducing manufacturing costs.
system structure
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the system architecture from the input end of the antenna to the output end of the SDIO interface connected to the host or multimedia processor component.
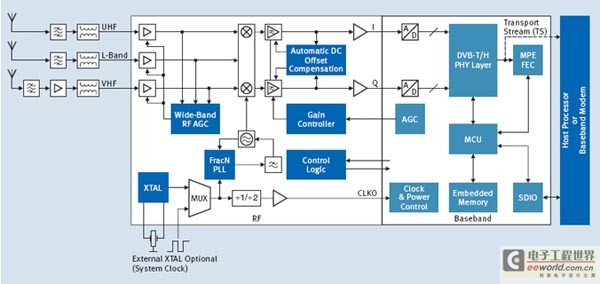
Figure 1: Functional architecture block diagram of OmniVia TUS9090
The first part of the front end that implements mobile TV functions is the small antenna required for RF signal reception. In the mobile environment, the recovery of mobile TV signals is limited by various conditions, including specific system integration issues. Taking into account factors such as the bandwidth of the UHF receiver and the size limitation of the mobile terminal antenna, the antenna design faces huge challenges. Although a low-noise receiver design can alleviate this problem, the antenna is still the best "low-noise amplifier" in the system. Therefore, we need to find novel antenna solutions. Tuned antennas or resonant antennas have very good performance. However, when the GSM transmitter emits a strong signal, because the isolation between the wireless component and the DVB-H antenna is only 10-20dB, nonlinear tuning components such as varactor diodes will reduce the quality of the useful signal.
The TUS9090 uses a compromise configuration, designed to achieve the best linearity and lowest noise. At the UHF level, the noise figure of the RF tuner is 4dB, which complies with the MBRAI II standard. If a certain application requires higher performance, the noise figure can be increased to 2dB or lower by adding an external LNA. Infineon can provide a complete reference design or modify the design according to the specific needs of customers.
In TUS9090, after the antenna and input stage is the embedded RF receiver, which is integrated LNA, mixer, channel filter, crystal oscillator, phase-locked loop (PLL) and on-chip loop filter, Direct conversion receiver for VCO and IF gain controller. The differential signal path from RF to I / Q signals has excellent noise suppression. In addition, the integrated broadband radio frequency AGC (automatic gain control) loop is located behind the integrated LNA. The RF component can be directly connected to the LNA to detect the signal. It can respond to all the signals that the mixer can detect, avoiding any linearity problems caused by any adjacent channels. For the broadband AGC, the TUS9090 uses an analog gain control loop to digitize the baseband gain control, and controls the programmable gain step size through a dedicated digital AGC bus. In addition, an integrated high-performance crystal oscillator that supports multiple standard crystal frequencies can ensure the normal operation of RF components-regardless of whether the system clock is available. However, this RF component can also work with a high-quality system clock to reduce the cost of the crystal.
Phenolic Paper Laminated Sheet is a hard, dense material made by applying heat and pressure to layers of paper or fabric, impregnated with a synthetic resin. These phenolics are approx half the weight of aluminum and their physical toughness resists abrasion, friction, impact, and material fatigue. Special properties fight off the corrosive action of water and many chemicals, increasing the service life and efficiency of your product parts. The insulating qualities of each grade, such as low dissipation factor and excellent dielectric strength, make them valuable for many precise electrical and electronic applications.
It is made of insulating impregnated paper impregnated with phenolic resin and baked and hot pressed. Has high mechanical properties. The heat resistance level is E level.
Phenolic Paper Laminated Sheet
Phenolic Paper,Phenolic Cardboard,Paper Phenolic Sheet,Phenolic Paper Laminated Sheet
Yingkou Dongyuan Electrical Insulation Board Co.,Ltd , https://www.dy-insulation.com