The PMBus (Power Management Bus) open standard specification defines a digital communication protocol for controlling power conversion and management devices. In systems where power requirements are complex, multiple DC/DC converters are typically used to generate the power requirements required for different semiconductor devices. One obvious result is that controlling and monitoring these power supplies becomes more complicated during product design, production testing, and daily use.
Currently, many high performance DC/DC converters are still controlled by analog signals generated by passive components. Even with the most advanced power circuit topologies, external potentiometers and capacitors have to be used to adjust parameters such as start-up time, output voltage value, and switching frequency, and these parameters cannot be changed at any time.
PMBus is an open standard digital power management protocol. The converter can communicate with other devices by defining transport and physical interfaces as well as command language. The PMBus transport layer is based on the low-cost SMBus (System Management Bus) version 1.1, which is a robust, industry-standard application-compliant I2C serial bus with group checksum and host notification.
PMBus inherits the SMBLERT signal of SMBus, which can cause the slave device to interrupt the control of the bus by the system host. This method reduces the burden on the system host and enables the host to perform closed-loop control most of the time. The way the microcontroller is queried is more flexible. In addition, the default configuration data of the PMBus protocol slave device is stored in the permanent memory or set in the hardware. In the process of power-on, the initial configuration information is not needed through the bus communication, which shortens the startup time and reduces the startup time. Part of the bus data transmission. In addition to the SMBus clock, data, and interrupt lines, the PMBus protocol specifies two hardware signals for use with power conversion devices. One is a control signal that is used in conjunction with commands issued by the bus to initiate and shut down individual slaves. The device; the other is an optional “write-protect†signal that prevents changes to the data in the slave device memory.
Unlike other buses, the PMBus master device is not a dedicated integrated circuit, which provides flexibility in the selection of master devices for power management. When the power system is relatively large, the PC can be configured with the corresponding data acquisition board to complete various management functions, while for the smaller power system, it can be a ready-made microprocessor on the board, and some additional low-cost Microcontrollers are some of the gates in PLD devices. Different devices can be used as hosts for PMBus at different stages of product development. In the board design phase, a portable computer can be used as the bus master; in the actual application of the product, some hardware resources in the on-board main processor are used to control the PMBus bus. In the development phase, the set values ​​and configurations in the slave devices can be dynamically modified through the PMBus bus. For different power systems, the same PMBus bus configuration can be borrowed, and only certain data needs to be modified. Finally, the set values ​​and configuration passed the test are permanently saved in the memory of the slave device by the write protection function. Figure 1 shows a typical connection structure diagram of digital power management based on PMBus.
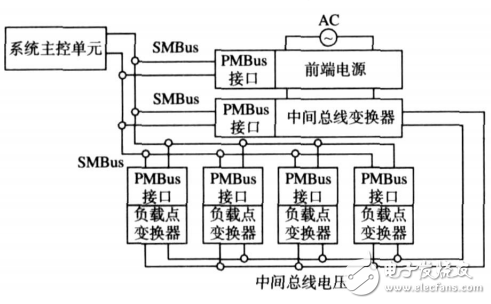
Figure 1 Typical connection structure diagram of digital power management based on PMBus
PMBus communication is done in a simple command set. Each packet contains an address byte, a command byte, a number of data bytes, and an optional packet check code byte. Figure 2 shows a host-to-converter information transfer. The host uses separate Start and Stop to indicate the start and end of the process. The slave device uses a separate bit to acknowledge each byte received.
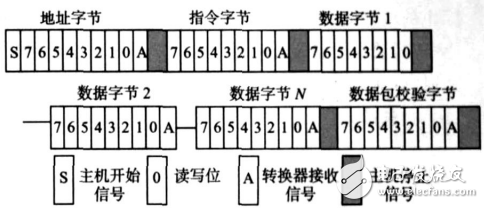
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of information transfer from a host to a converter
Unlike other bus protocols, the PMBus bus does not wait for a dedicated "execute" command. The slave device processes and executes the command as soon as it receives the "stop" signal, meeting the rapidity requirements of power management. Due to its openness and advancement at the beginning of development, the instruction set supported by the PMBus bus protocol can provide an extension of two commands that effectively allow double-byte commands. One extension is reserved for the manufacturer of the PMBus device, and the other extension is due to subsequent upgrades and revisions of the protocol itself. In practical applications, the simple and practical instruction set of the PMBus protocol makes the writing of power management programs faster and easier. The implementation of voltage timing control for point-of-load converters is a good example. The power-up sequence control corresponds to two PMBus commands, the TON_DE2LAY command sets the time the converter waits to start power-up, and the TON_RISE sets the time from zero to the set output value. Therefore, the user can set the startup delay and rise time of each converter through the relevant software. Similarly, for the power-down sequence control, there are also corresponding power-down delay commands TOFF_DELAY and fall time TOFF_FALL settings. Obviously, the timing control for the start and power down of the entire power supply system usually only requires 4 PMBus commands to set. PMBus has been recognized by the industry.
Northwestern Polytechnical University Chen Lin Li Shuqin Lin Hui
Cummins Diesel Generator assembly by Cummins diesel engine, alternator, radiator, controller, base frame;
. World Famous diesel engine brand: Cummins,
. World famous AC alternator brand: Stamford, Leroy Somer, Mecc Alte, Marathon, Faraday, SWT
. World famous genset controller brand: Deepsea, ComAp, Deif, SmartGen,
. Good Quality Cooling Radiator
. Start Battery system
Cummins Engine,Cummins Generator Set,Cummins Power Generator,Cummins Diesel Generator
Guangdong Superwatt Power Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.swtgenset.com