For VR (including MR) devices, the screen is a critical part of the experience, such as the resolution, refresh rate and other parameters, directly determine whether the experience can enjoy the virtual world in a comfortable, clear way after the display.
The user complained that the VR head showed the most sensation of vertigo in addition to weight, which was due to the low screen refresh rate. The sights we see and delays, and the resulting sense of incompatibility, can cause dizziness, so the current mainstream refresh rate is above 90Hz to ensure low latency.

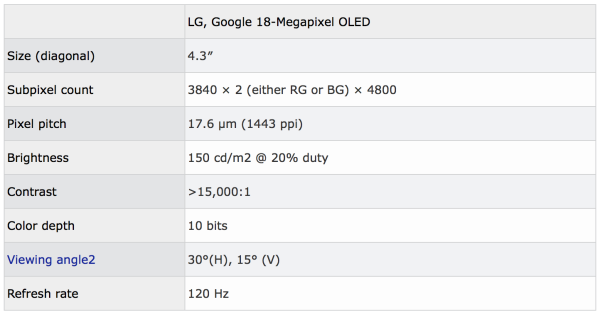
LG and Google worked together to improve the VR device display technology and jointly created a 4.3-inch OLED display with resolution up to 4800x3840 (1443ppi) and 120Hz refresh rate. According to foreign media reports recently, LG and Google published a research paper introducing the details of more new screens.
The authors of the paper stated that they are trying to create OLED panels that are closer to the human visual system. Thus designing an OLED display with a field of view angle higher than 100 degrees (current designs providing up to 120 degrees of horizontal FoV and 96 degrees of vertical FoV), 1000 to 2200 pixels per inch (PPI), and a monocular 15 to 25 megapixel OLED display. In contrast, the current HTC Vive Pro, Samsung Turion MR head display is used in the 90Hz refresh rate, monocular 1440x1600 resolution screen.
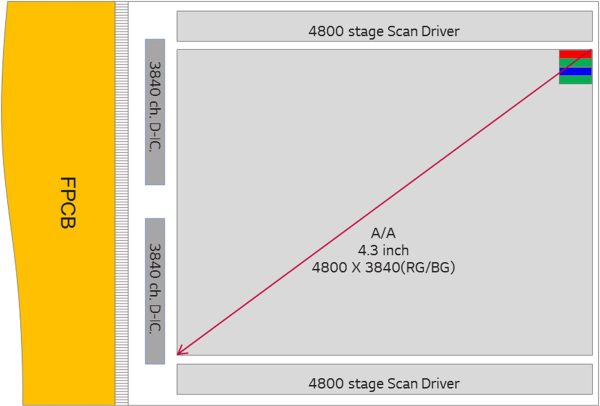
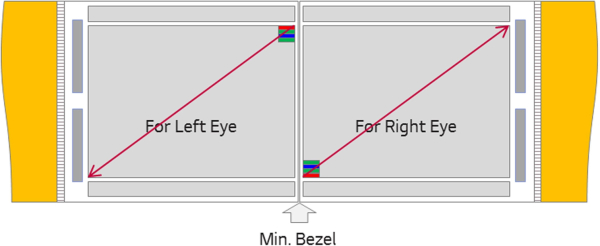
LG and Google's engineering team designed two 18-megapixel screens for VR headshots. In addition to the middle of the two screens, the 4.3-inch panel has electronic components on three sides and a 1.7-mm bezel on the side.
However, it is worth mentioning that this is not the team’s “ultimate goalâ€. The author of the paper mentioned that the theoretical upper limit is 9600×9000 pixels (2183ppi) and 150°+160°FoV. Of course, such high-resolution screens also need strong hardware to support. It is still difficult to see high-resolution products on mobile devices for some time, but the PC side can still look forward to.
LG and Google engineers also focused on finding ways to help GPU drive 18 million pixel displays. The team created a center rendering technique that broke the image into two sharpness levels. The high-sensitivity area responds to the user's possible visual high-frequency areas, which are presented at full resolution (relatively small); for users with less gaze, are presented at a lower level of detail to save the required bandwidth for rendering.
The display panel has a built-in FPGA that combines low-frequency and high-frequency data to create a full-screen image. Low-frequency visual areas are displayed at 1280x1922 pixels, and the FPGA scales them up to the panel resolution.
Stator Core welding is a important process for stator core assembly. We are able to use TIG, MIG, LASER weld to meet different requirement for customers. The stator core is an important part of the stator and the main component of the magnetic circuit of the motor. Different sizes of stator cores have different technological processes and application fields. For example, small-sized stator cores are usually assembled by interlocking, and the outer diameter is usually less than 200mm. Large-sized stators are assembled in different ways depending on the motor design, such as stator core by cleating and staor core by welding.
Stator Core By Welding,Stator Iron Core,Bldc Stator Core,Laminated Stator Core
Henan Yongrong Power Co., Ltd , https://www.hnyongrongglobal.com