The basic concept of timing analysis to be introduced today is skew, which we call deviation. Since the path delay of the clock to each register is different, the time for the signal to reach the clock pin is also different. We call the time deviation of the clock signal to the different registers as skew. Skew has always been an important parameter to measure the performance of the clock tree. The purpose of traditional CTS is to reduce skew.
There are many types of skew . According to the direction of clock and data path, skew can be divided into positive skew and negative skew . As shown below:
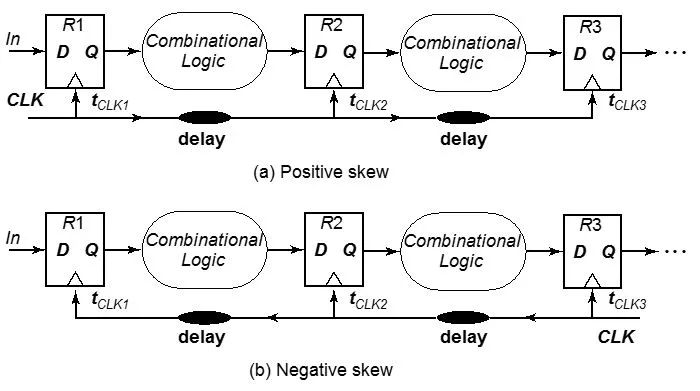
For positive skew, clock and data path are in the same direction. On the contrary, for negative skew, clock and data path are in opposite directions. What impact do they have on our design? Let's take a look at the calculation formula of setup and hold:
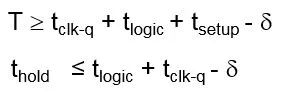
We can get the following results,
For positive skew, it can reduce the T time, which is equivalent to improving the chip's performace. But its hold time will become more difficult to satisfy
For negative skew, its hold time is easier to meet, and instead, it will reduce the performance of the chip.
There is another skew classification method, which is more common to us. According to the clock domain and path relationship, skew can be divided into global skew , local skew , and interclock skew .
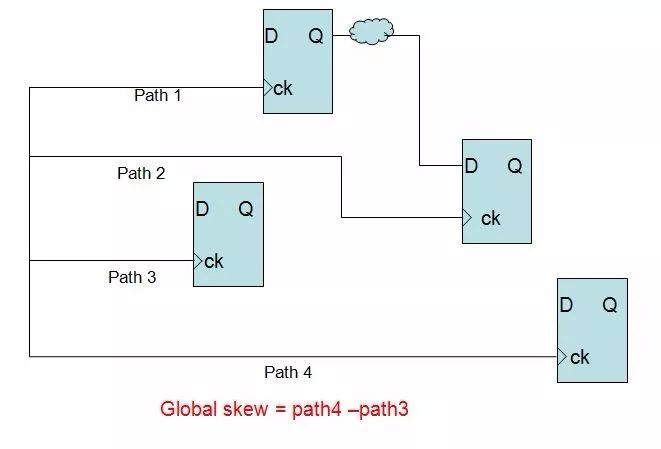
Global skew refers to the maximum skew of any two paths in the same clock domain. As shown in the figure below, note that any two paths, whether it is a timing path or not, will be counted as objects for gloabl skew calculations. In CTS, the tool pays more attention to global skew, and will make global skew as small as possible.
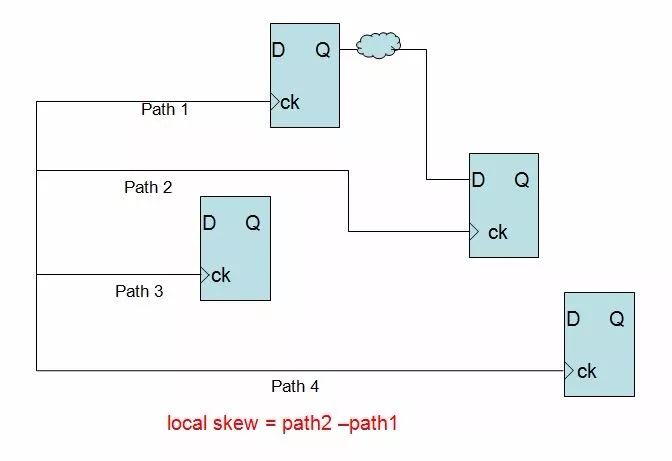
Local skew refers to the maximum skew of any two logically related paths in the same clock domain. It needs to be noted here that the local skew must be calculated only if there is a logical relationship path, which means it must be a timing path. As shown in the figure below, when we analyze timing, we pay more attention to local skew.
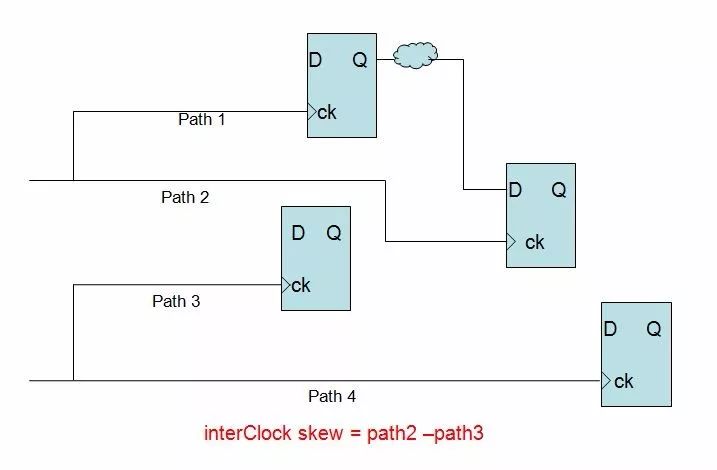
InterClock skew refers to the maximum skew of the path between different clock domains, as shown in the figure below:
In addition, there is a more special envoy skew, which is the more useful skew, which we call useful deviation . Generally speaking, skew will deteriorate the timing result, but if used reasonably, skew can also play a role in repairing the timing, thereby increasing the frequency of the design.
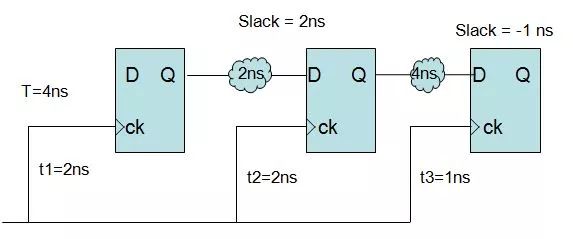
As shown in the figure below: The clock cycle is 4ns, and the delay of each clock path is as follows: You can see that there is a path with a slack of -1ns, indicating that this path violates regulations. You can see that the skew related to this path is t3-t2= -1ns.
Next, we use useful skew to borrow 1ns of time from the previous slack path (slack=2ns), so that both paths meet the timing requirements. As shown below:
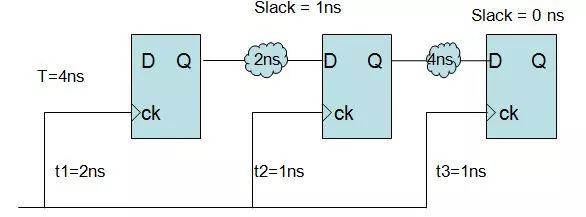
This is the function of useful skew. You can borrow time forward or backward to correct violations.
Ic Pmic,Pmic Full Half Bridge Drivers,Pmic Gate Drivers,Integrated Circuits Ics Pmic
Shenzhen Kaixuanye Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.iconlinekxys.com